Bundle analysis
Introduction
Rsdoctor provides the Bundle Size module, which is mainly used to analyze the information of the build artifacts of Webpack or Rspack, including the size of resources, duplicate packages, and module reference relationships:
- Bundle Overview: Displays the total number and size of artifacts, as well as the number and size of each file type. It also shows the duplicate packages and their reference chains.
- Bundle Analysis Module: Analyzes the size and code information of the build artifacts' resources (Assets) and the included Modules. In this module, you can view the actual code size of modules after packaging in the Assets, as well as the original code or packaged code segments and module reference relationships.
Click on the "Bundle Size" option in the navigation bar to view the Bundle analysis report. Please note that to display this page, you need to enable the build artifact analysis capability features.
Glossary
Assets: Resources refer to images, fonts, media, and other file types. They are the files that ultimately exist in the output folder. Each Chunk has corresponding Assets resources.Module: One or more Modules combine to form a Chunk. For more information about Module types, please refer to Rspack Modules and Webpack Modules.Bundle Size: The final packaged size of the resource artifact, which is the final size after being processed by the bundler.Module Bundled Source & Size: Module Parsed Source refers to the final code fragment of the Module in the packaged artifact, and Module Parsed Size refers to the size of the final code fragment of the Module in the packaged artifact.Package Count: The number of third-party packages.Initial Chunk: The initial chunk is the main chunk of the entry point. This chunk contains all the modules specified by the entry point and their dependencies, unlike the chunks for "on-demand loading".- For more information about Initial Chunk, please refer to Initial Chunk Introduction.
Duplicate Packages: Duplicate third-party packages bundled into the project. Excludes third-party packages that are not bundled into the artifact. Please refer to Duplicate Packages.Concatenated Module: A concatenated module is a technique that combines multiple modules into one closure during packaging. In the past, Rspack would package each module into a separate closure, and this encapsulation function would cause slower execution of JavaScript in the browser. Optimization can be achieved by enabling theoptimization.concatenateModulesparameter.
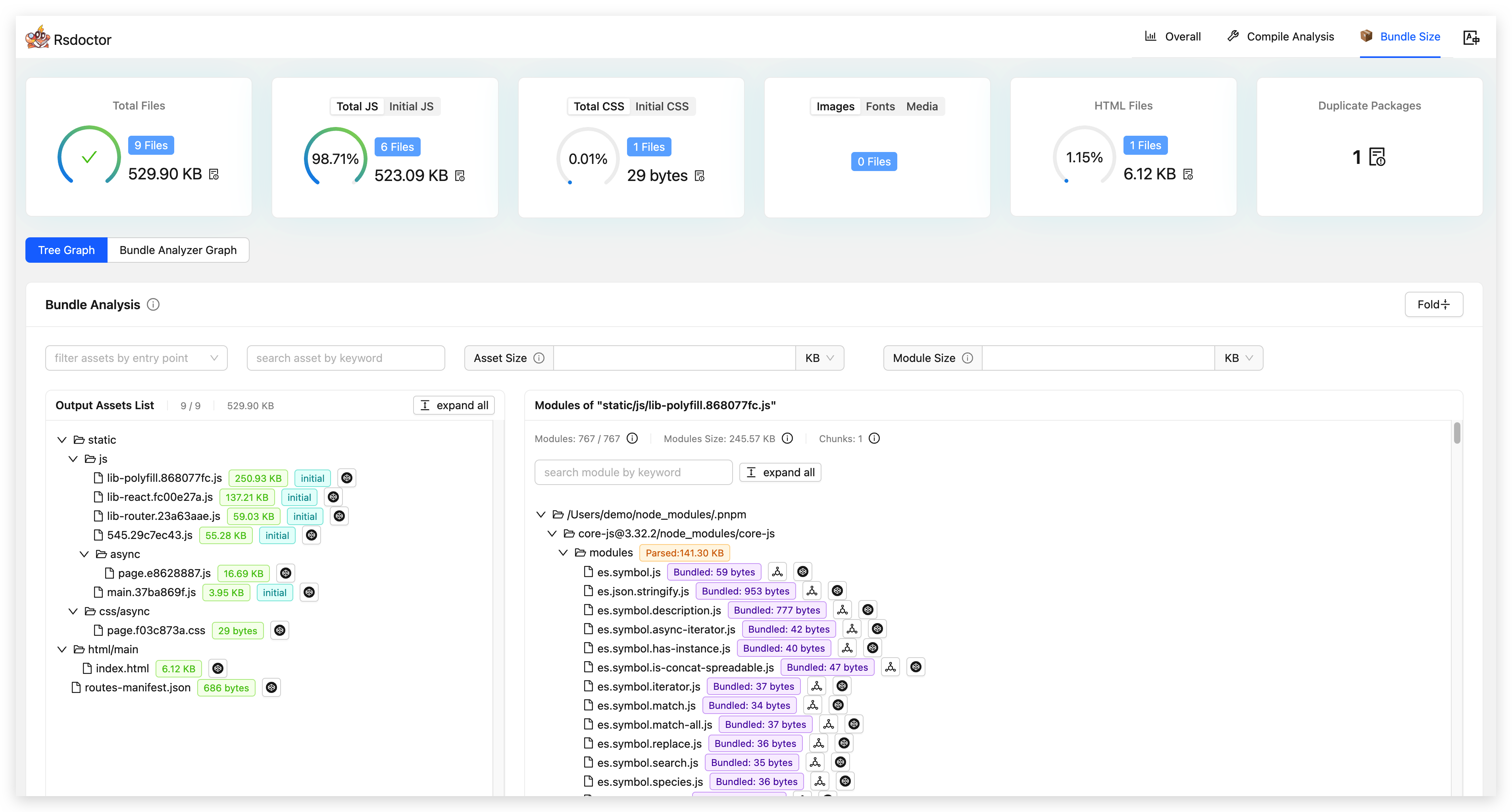
Bundle overview
Bundle information card
The bundle overview displays information about the number and size of files, such as Total Files. Clicking on the card chart expands the resource details, as shown in the following image:
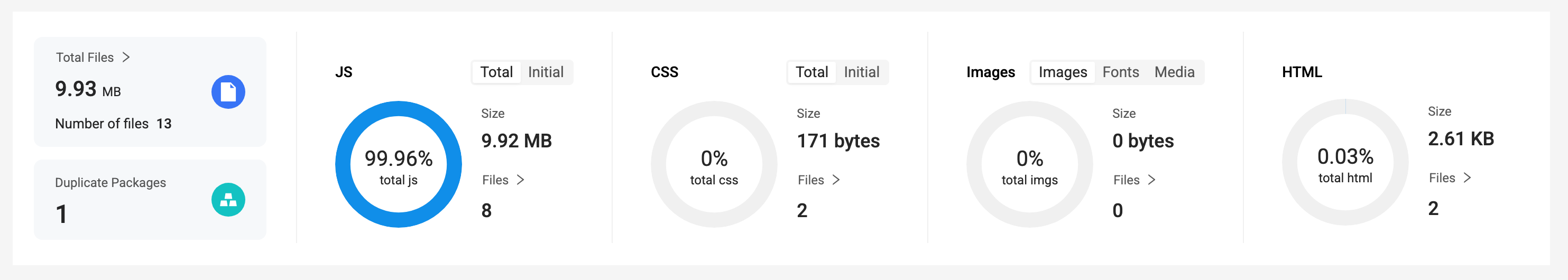
- Clicking on the details icon displays the corresponding resource tree on the right, indicating the resource sizes:
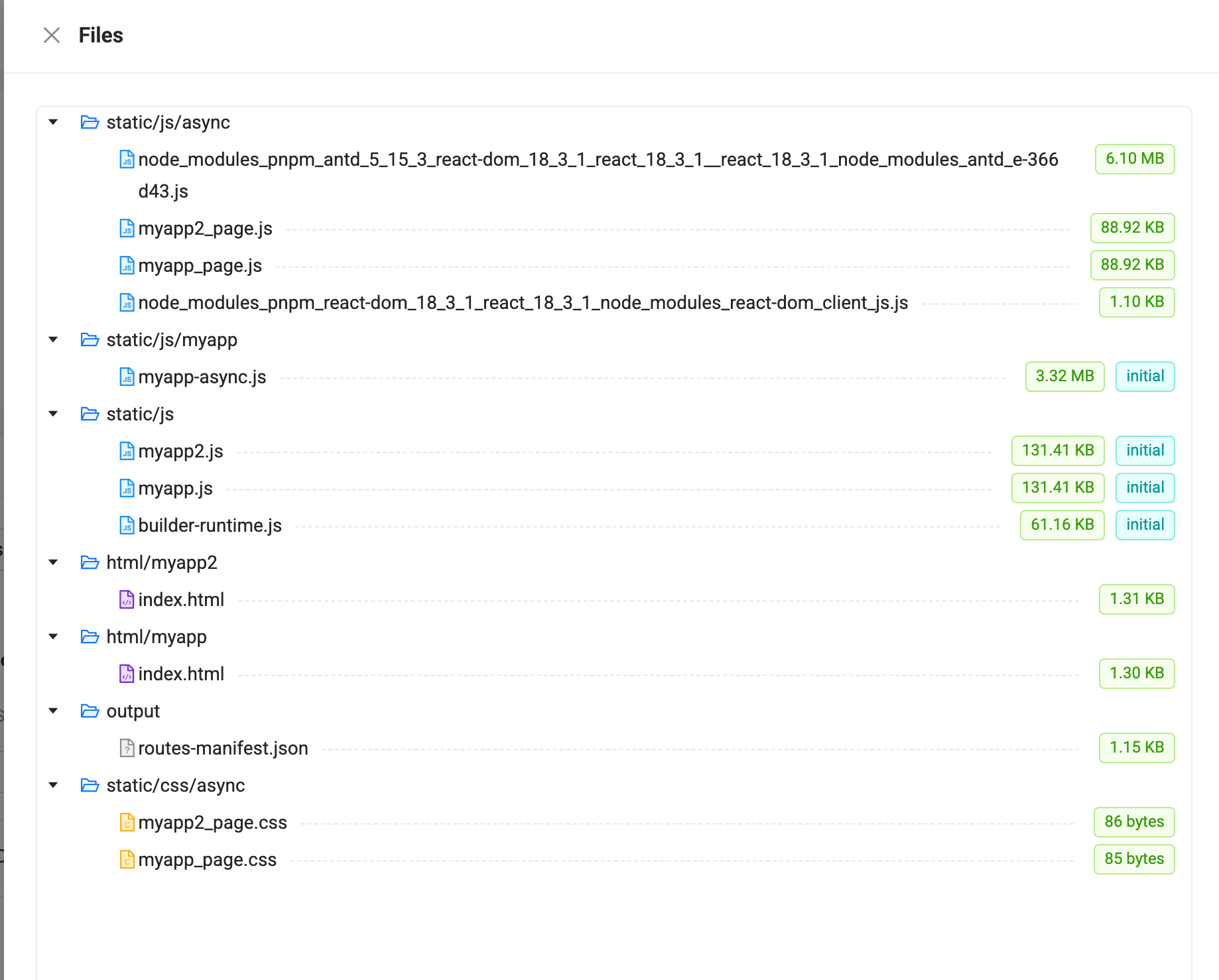
- Clicking on the tabs allows you to switch between different resource information views, such as [Total JS | Initial JS]. The card also displays the percentage, size, and number of resources. Similarly, clicking on the icon in the lower right corner expands the resource list.
Duplicate packages
The Duplicate Packages card displays the number of duplicate third-party packages in the project. Clicking on the image allows you to view the specific details of the duplicate packages. Please note that these are duplicate packages that have been bundled.
For more information, please refer to Duplicate Packages.
Bundle analysis
If your project is based on Rspack and the version is lower than 0.5.1, you cannot view code information.
Resource and module relationship display
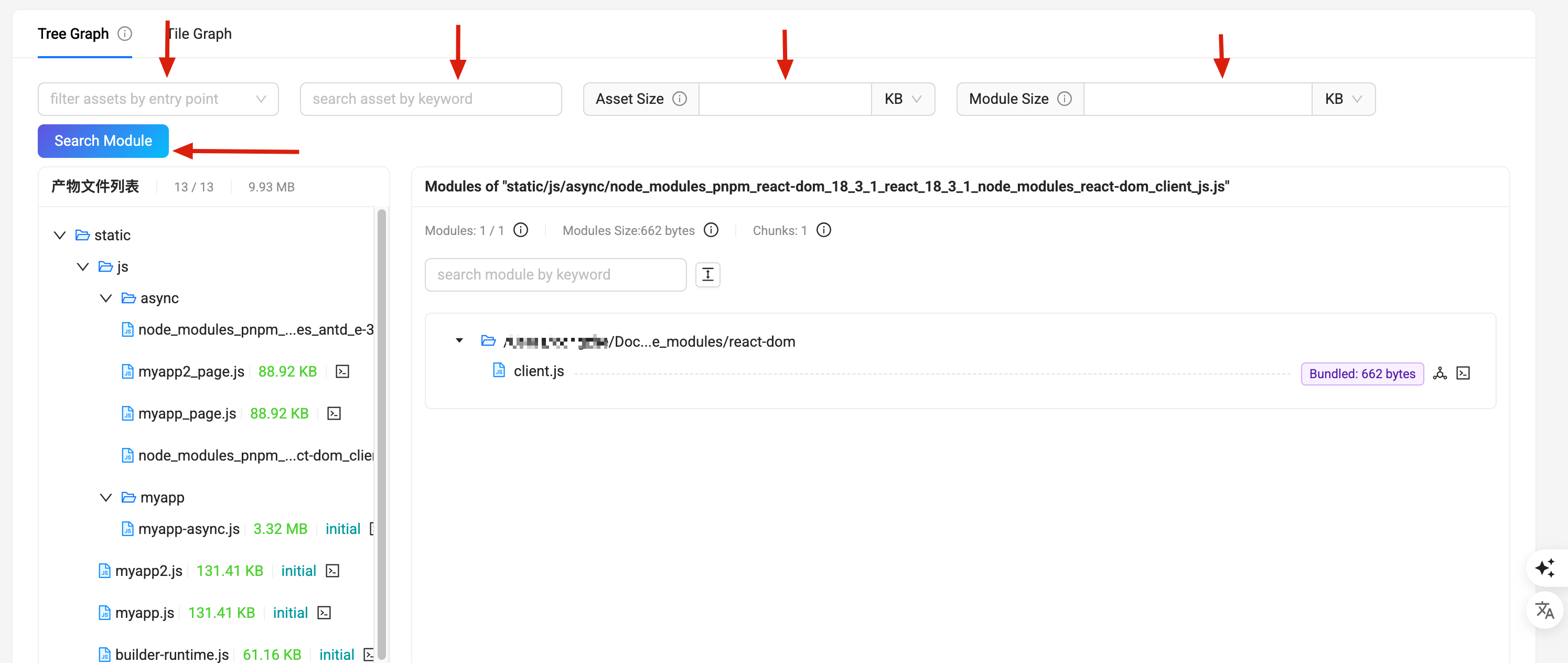
The Bundle Analysis module is used to analyze the size and code information of the build artifacts' resources (Assets) and the included Modules. The example image is shown below:
- On the left side is the list of Assets resources, sorted in descending order by resource size. You can click the "expand all" button to expand all nodes.
- On the right side is the list of Modules corresponding to the Assets, also sorted in descending order by module size after packaging.
Search and filter box
The top toolbar from left to right includes: the search tool for Assets, the filter tool for Assets size, and the filter tool for Module size.
- Search Entry Input Box: Enter the keyword of an Entry in the input box to search for the corresponding Entry and display only the related Assets.
- Search Assets Input Box: Enter the keyword of an Assets in the input box to search for the corresponding Assets.
- Assets Size Filter Tool: Enter a number with units of KB or MB to filter out Assets resources smaller than the specified size.
- Module Size Filter Tool: Enter a number with units of KB or MB to filter out Module resources smaller than the specified size.
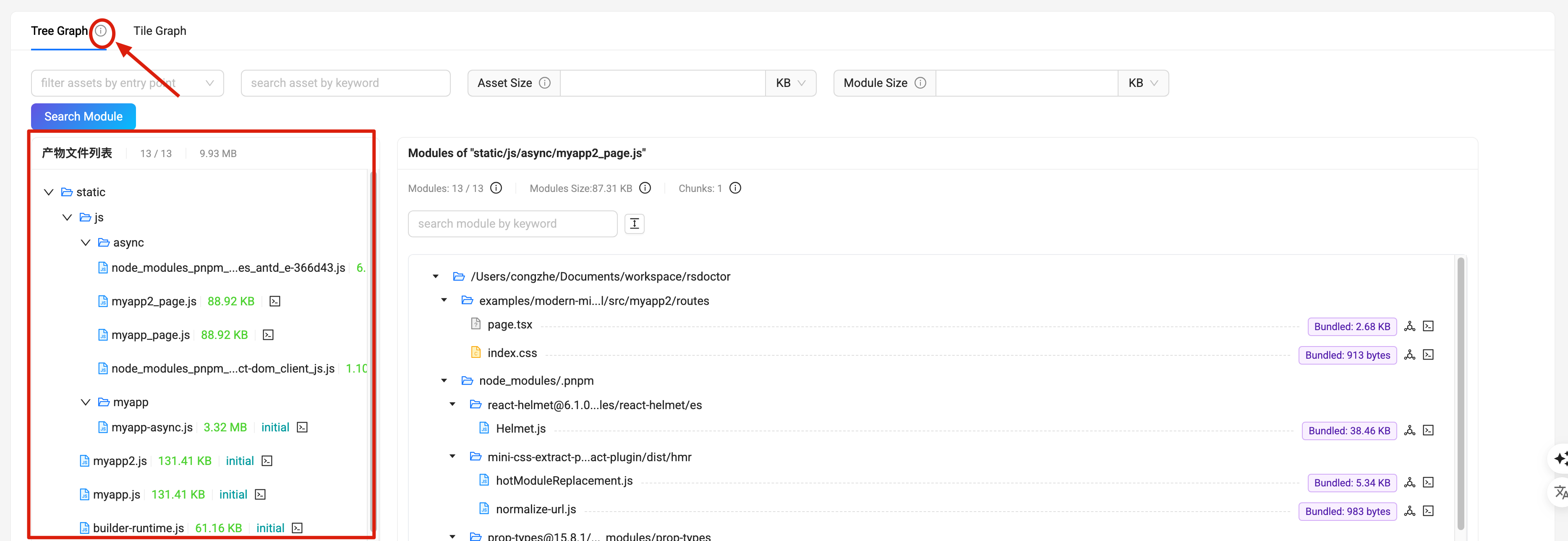
Search module
Search for which Assets the Module is located in. As shown in the figure, you can see the results of matching the search Module keyword.
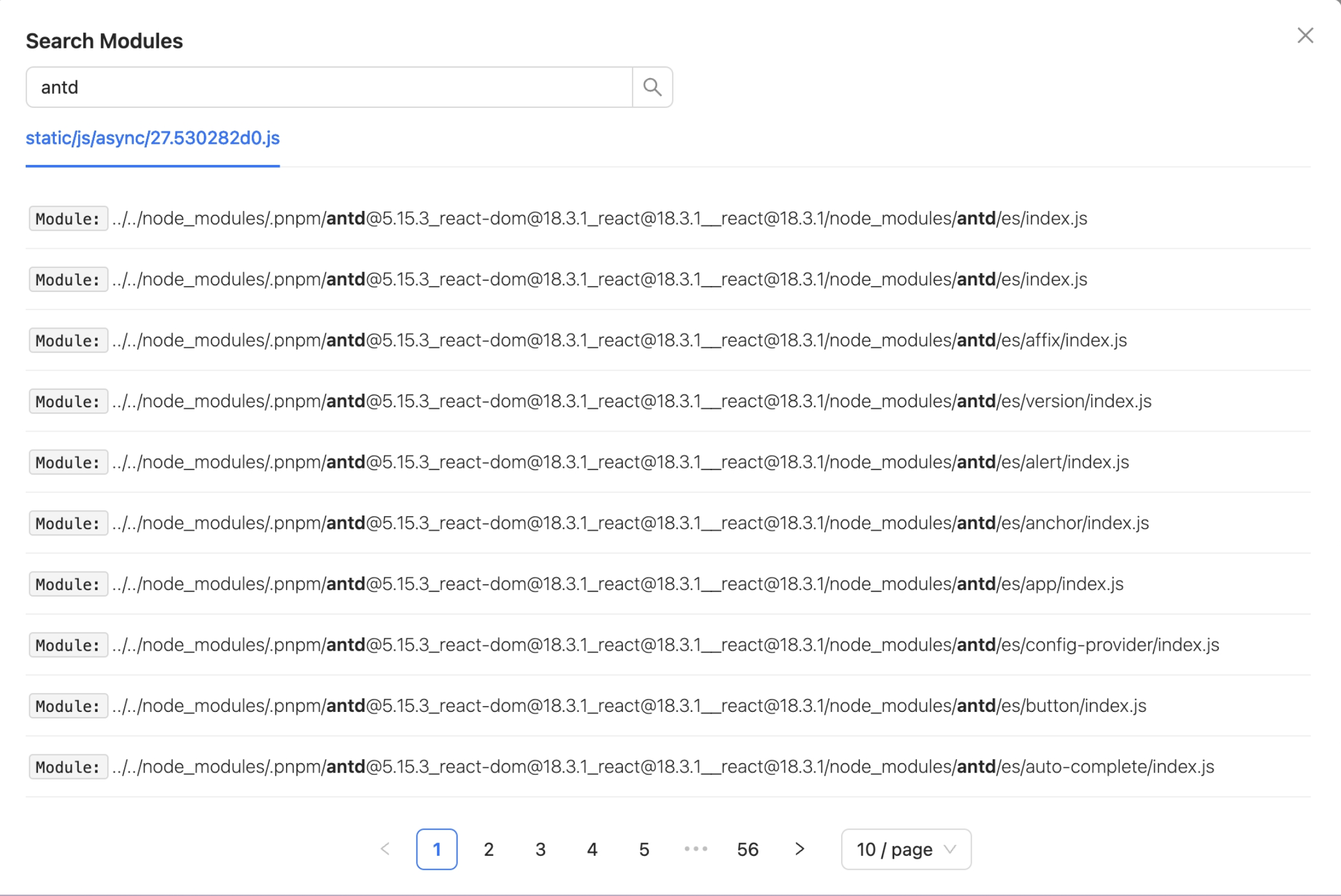
Search module
The module search functionality is supported, allowing users to click the "Search Module" button to open the module search dialog. By entering the module name, users can quickly locate and view the module's position in the Assets, making it easier to analyze the module's reference relationships and size. The search determines which Assets the Module is located in.
As shown in the following image, the results of matching the search Module keyword can be seen:

Module tag explanation
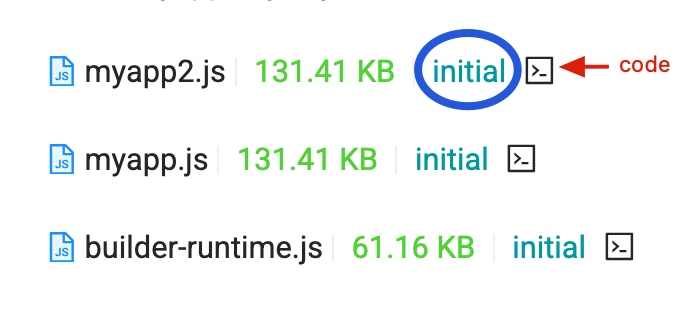
The Assets tag is shown in the left image, from left to right representing: Resource Size, Initial Chunk, and Code View.
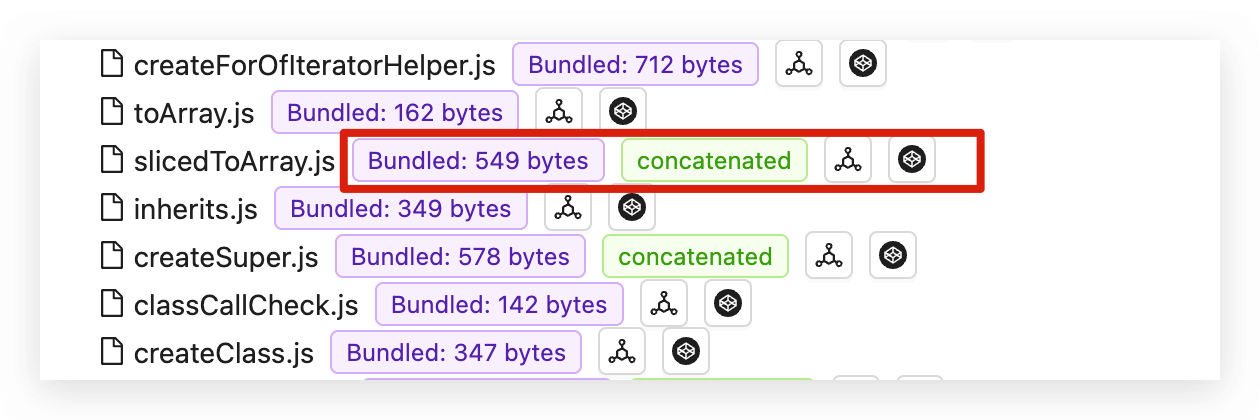
The Modules tag is shown in the right image, from left to right representing:
- Bundled Size
- The final size of the module bundled into the artifact. Some modules labeled as
concatenatedare concatenated modules, which have a certain impact on this value. Please refer to the explanation ofconcatenated modulebelow.
- The final size of the module bundled into the artifact. Some modules labeled as
- Concatenated Module: Concatenated modules are modules that are optimized or concatenated into one closure during bundling. There are two types:
- One is the concatenated main module, indicating how many
Modulesare concatenated. - The other is the concatenated sub-module, indicating which
Moduleit is aggregated into. This sub-module cannot be further unpacked after bundling, so the specificBundled Sizecannot be determined. Only the size of the entire concatenated module is known, which is marked at the end of the main module.
- One is the concatenated main module, indicating how many
- Module Explorer tag: Click to open the dependency analysis page between
Modules. - Code View tag: Click to expand code segments, including
Source(source code),Transformed(compiled code), andBundled(bundled code).
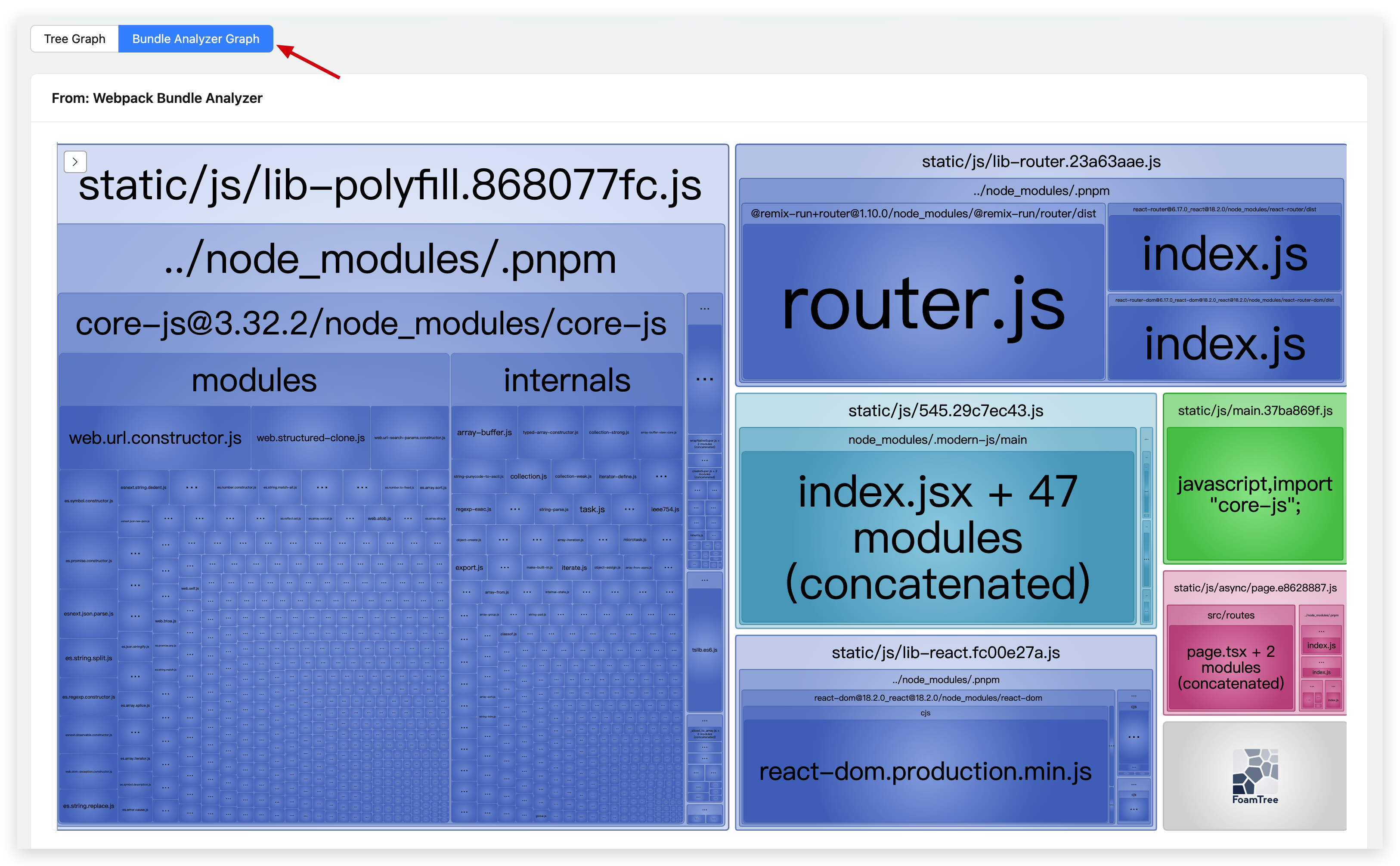
Bundle overview tile graph
Click the "Bundle Analyzer Graph" button on the "Bundle Size" page to view the classic tile graph.
Supports BannerPlugin
supports.banner option is only used for debugging, do not use it in production.
Both Rspack and webpack support the BannerPlugin, which is a built-in plugin that allows you to add specific content at the top or bottom of the generated chunks.
The added code segment will affect the analysis capability of the bundle.
Rsdoctor is compatible with the logic of adding code using the BannerPlugin, but it is not enabled by default because Rsdoctor needs to add tag code. The Rsdoctor BannerPlugin capability is enabled in the following two cases:
-
The project uses the BannerPlugin in
rspack.config.(js|ts)orwebpack.config.(js|ts). -
Enable Rsdoctor BannerPlugin capability through Rsdoctor options by setting
supports.banner:
- Note: Enabling
drop_consolewill affect Rsdoctor's analysis of the BannerPlugin. Therefore, you can disabledrop_consolewhenRSDOCTOR = true.

